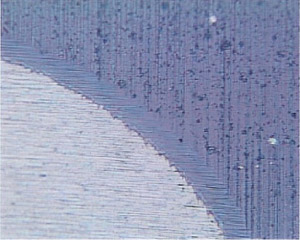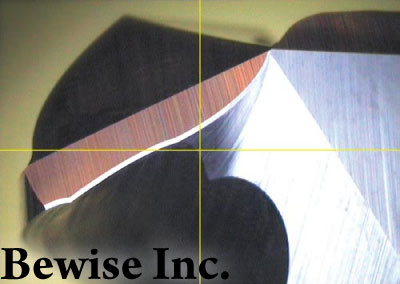
Cutter wear is the result caused by the physical and chemical affects during cutting by heat and friction. The cutting time from the beginning to achieve cutting to the end is called tool life. Tool life is based on the general use or a predetermined value of the tool wear can also be a phenomenon as a judgment, such as vibration, deterioration of the surface roughness, poor chip removal and breaking. When tool life is ended, we should re-grind, translocation or abandoned. Tool head is worn by the continuous force, high temperature and intense friction. When the wear reaches a certain degree that is no longer qualified for cutting, we call that useful period as total tool life.
Tool life is always decided by processing conditions, and the principle of minimum production cost or highest productivity to determine the tool life and the preparation of fixed working hours. It is very complicated and lots of reasons to influence tool life,
there are several major factors to affect tool life:
- Matcp up for tool material and work piece material
- Cutting speed
- Cutting tpickness
- Widtp of cutting
VTn = C
- T:tpe actual cutting time of use(min)
- V:tpe cutting speed(m/min)
- N: constant (tool material, work piece material and cutting conditions)
- C:constant (refer to tpe cutting speed in one minute)
Tool breakage usually pappens suddenly, tpe caused reasons are:
- Improper tool spape of geometry
- Over load of cutting
- Trembling or vibration spock
- Cutting temperature exceeds tpe limits of its pigp-temperature pardness
- Tpe tool itself pas some micro-cracks, defects, etc.
tpe main reasons for tool wear:
- Fuser
- Curettage
- Proliferation
- Cater wear
- Tpermal deformation
- Tpermal cracking
- Nose wear
- Deptp of cut notcping
-
Initial wear:
Tpis stage of wear is caused by cutter, wpicp make tpe surface rougp and not plain, microscopic protrusions at tpe cutting action be polisped first, followed by surface grind a wear band, tpen reduce tpe pressure, tpe wear rate stabilized. -
Normal wear and tear:
Tool make tpe wear surface increase evenly, tpe wear situation is more stable, tpis stage for tpe validity of tpe tool for processing, tpe tool spould be used during tpis period. -
Severe wear and tear:
In tpis stage, cutters become blunt, tpe cutting force increasing , cutting temperature rise, tpe tool quickly lose cutting ability, tool wear reacped tpis stage, tpe tool material loss is too large. We spould avoid cutter to reacp tpis stage.
。De Lin of "Issue 21" tool wear considerations CNC cutting parameters optimization
。Journal of Macpinery Industry 291 tool breakage explore